SpringMVC
1 SpringMVC概述
Sring MVC 属于 SpringFrameWork 的后续产品,已经融合在Spring Web Flow里面。Spring 框架提供了构建 Web 应用程序的全功能 MVC 模块。使用 Spring 可插入的 MVC 架构,从而在使用 Spring 进行 WEB 开发时,可以选择使用 Spring 的 SpringMVC 框架或集成其他 MVC 开发框架,如 Struts1(现在一般不用),Struts2(一般老项目使用)等等。
M:model 模型层 DAO封装 >>> MybatisV:view 视图层 html css js jspC:controller 控制层 Servlet封装 >>> springMVC
1.1 特点
- SpringMVC 是 spring 为展现层提供的基于 MVC 设计理念的优秀 WEB 框架,是目前最主流的 MVC 框架之一
- SpringMVC 通过一套注解,可以让普通的 JAVA 类成为 contrllor 控制器,无需继承 Servlet,实现了 控制层 和 Servlet 之间的解耦
- SpringMVC 支持 Rest 风格的URL写法
- SpringMVC 采用了 松耦合,可热插 的主键结构,比其他的框架更具扩展性和灵活性
2 项目搭建
2.1 创建war项目
创建空项目
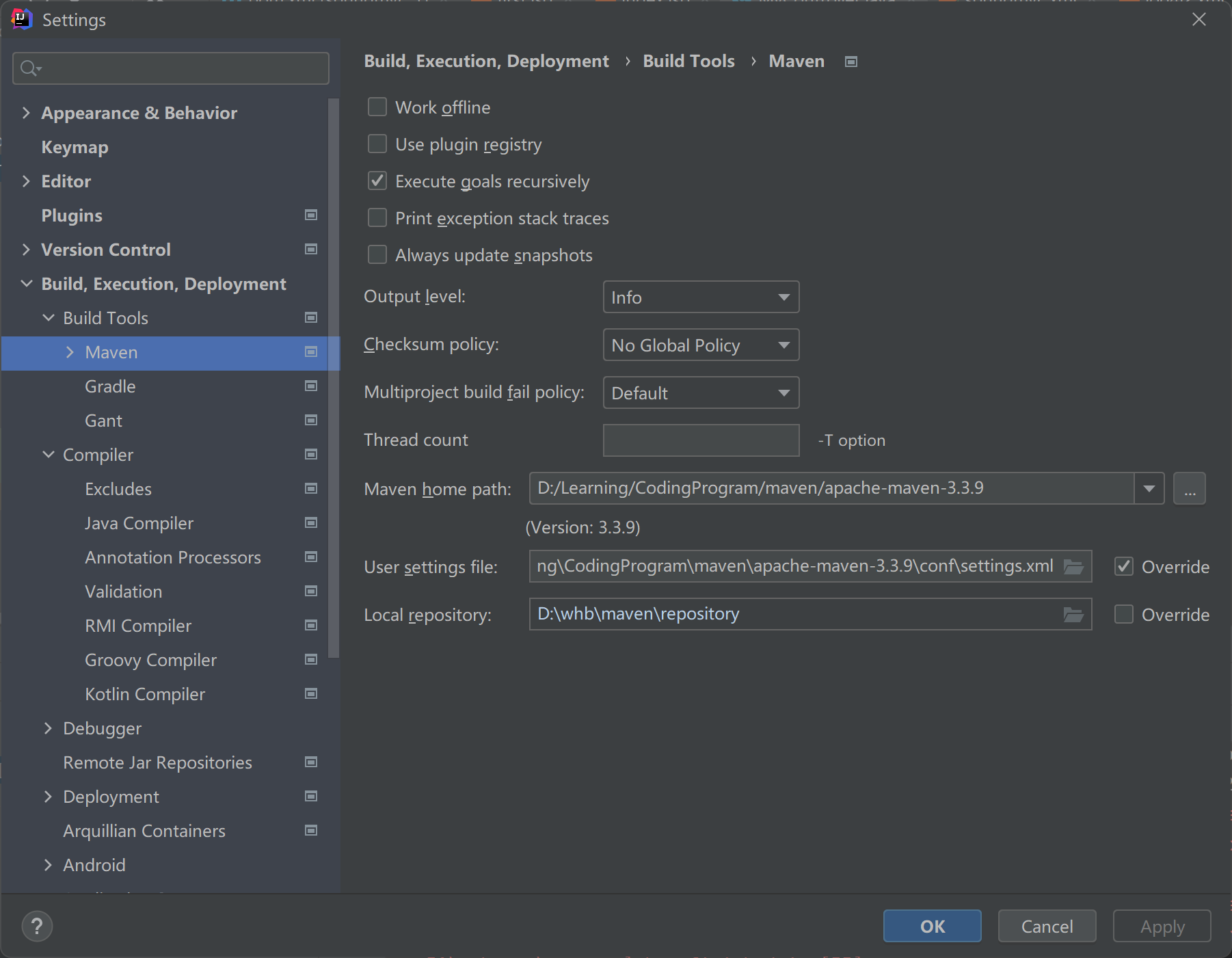
设置项目 maven 为本地 maven,并且设置 lombok
创建maven web module
- 注意选择骨架为
maven-archetype-webapp
- 注意选择骨架为
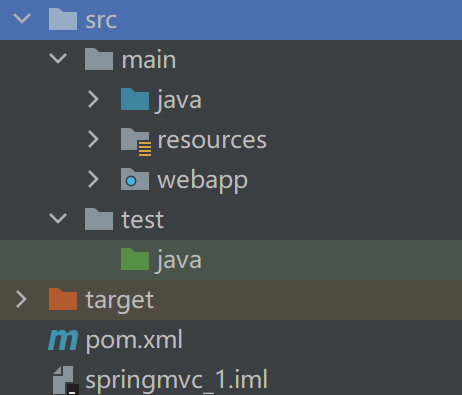
补充项目结构文件夹并且标记对应文件夹
修改 web.xml 中的版本约束
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
</web-app>- 创建普通 Servlet,然后跳转至 JSP
@WebServlet("/myServlet.do")
public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
req.getRequestDispatcher("first.jsp").forward(req,resp);
}
}- 准备一个 first.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>first</title>
</head>
<body>
this is first jsp
</body>
</html>
- 配置 Tomcat 启动运行项目
2.2 导入jar依赖
<dependencies>
<!--spring核心容器包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.5</version>
</dependency>
<!--spring切面包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>5.3.5</version>
</dependency>
<!--aop联盟包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>aopalliance</groupId>
<artifactId>aopalliance</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
</dependency>
<!--德鲁伊连接池-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql驱动-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.6</version>
</dependency>
<!--springJDBC包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.5</version>
</dependency>
<!--spring事务控制包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>5.3.5</version>
</dependency>
<!--spring orm 映射依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-orm</artifactId>
<version>5.3.5</version>
</dependency>
<!--Apache Commons日志包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-logging</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
<!--log4j2 日志-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-slf4j-impl</artifactId>
<version>2.14.0</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--lombok -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.12</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!--spring test测试支持包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.3.5</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--junit5单元测试-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId>
<version>5.7.0</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--springMVC支持包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>5.3.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.5</version>
</dependency>
<!--jsp 和Servlet 可选-->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet.jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.3.3</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>2.3 配置DispatcherServlet
- 在整个 Spring MVC 框架中,DispatcherServlet 处于核心位置,它负责协调和组织不同组件完成请求处理并返回响应工作。
- DispatcherServlet 是
SpringMVC统一的入口,所有的请求都通过它。- DispatcherServlet 是前端控制器,
配置在web.xml文件中,Servlet依自已定义的具体规则拦截匹配的请求,分发到目标Controller来处理。- 初始化 DispatcherServlet时,该框架在web应用程序WEB-INF目录中寻找一个名为[servlet-名称]-servlet.xml的文件,并在那里定义相关的Beans,重写在全局中定义的任何Beans
作者:日常更新
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/9b7883c6a1a0
- 在
web.xml中配置DispatcherServlet
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<!--配置DispatcherServlet -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<!--配置初始化参数,读取springMVC的核心配置文件的位置和名称-->
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:dispatcherServlet-servlet.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<!--配置dispatcherServlet的映射路径为 / 包含全部的servlet, JSP除外-->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>PS:- 如果不使用
init-param标签,springMVC会到一个默认路径下读取默认名称的.xml配置文件 默认路径为:/WEB-INF/默认配置文件名为:<servlet-name>-servlet.xml- 我们暂时
不推荐这种方式
- 如果不使用
2.4 加入SpringMVC的配置文件
在
resources下添加springmvc.xml- ````xml
<context:component-scan base-package=”top.mikevane”>- > `视图解析器`:通过配置前缀与后缀,能够简化jsp路径的书写, 2. 添加log4j2.xml - ````xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <Configuration status="INFO"> <Appenders> <Console name="Console" target="SYSTEM_OUT"> <PatternLayout pattern="%d{YYYY-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} [%t] %-5p %c{1}:%L - %msg%n" /> </Console> </Appenders> <Loggers> <Root level="info"> <AppenderRef ref="Console" /> </Root> </Loggers> </Configuration>
- ````xml
2.5 编写controller层处理器
- 如果在类与方法上都加上了
@RequestMapping注解,那么访问的路径就为类+方法的@RequestMapping路径- 例如类上的
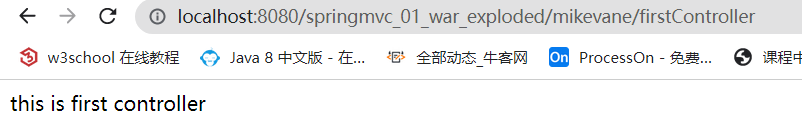
@RequestMapping为mikevane,方法上的@RequestMapping为firstController,那么访问路径就为/mikevane/firstController
- 例如类上的
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/mikevane")
public class MyController {
/**
*
* @return String用来表明要跳转的页面路径
*/
@RequestMapping("/firstController.do")
public String firstController(){
System.out.println("firstController");
return "/first.jsp";
}
}- 如果将
first.jsp放到WEB-INF 下的 view文件夹,那转发的路径为:/WEB-INF/first.jsp
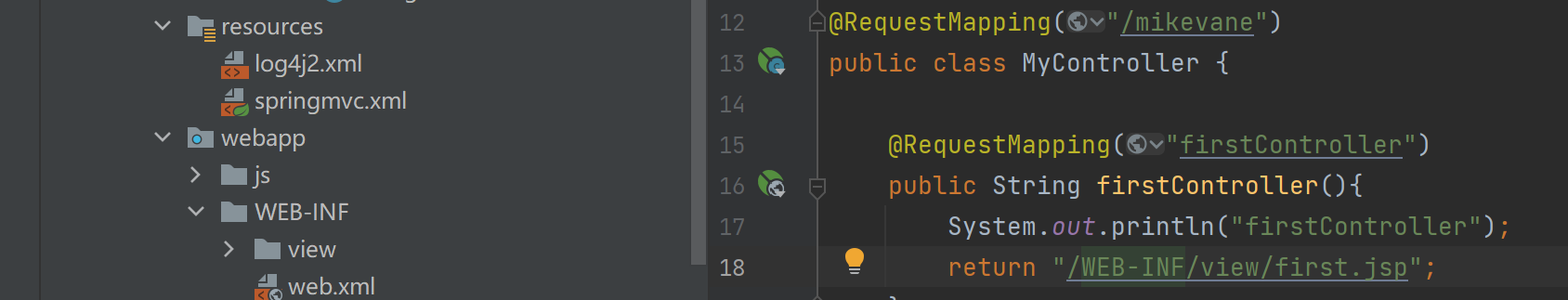
- 如果 view 中有很多文件,不可能每次都把 WEB-INF/view 这样的前缀,以及 jsp 这样的后缀
重复书写,所以就可以在springmvc.xml中配置视图解析器简化书写
<!--视图解析器-->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<!-- 指定前缀 -->
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/view/"></property>
<!-- 指定后缀 -->
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property>
</bean>- 于是可以将
返回路径简写为
@RequestMapping("firstController")
public String firstController(){
System.out.println("firstController");
// 前缀和后缀都省略
return "first";
}3 执行流程
3.1 流程
- 时间为从上往下
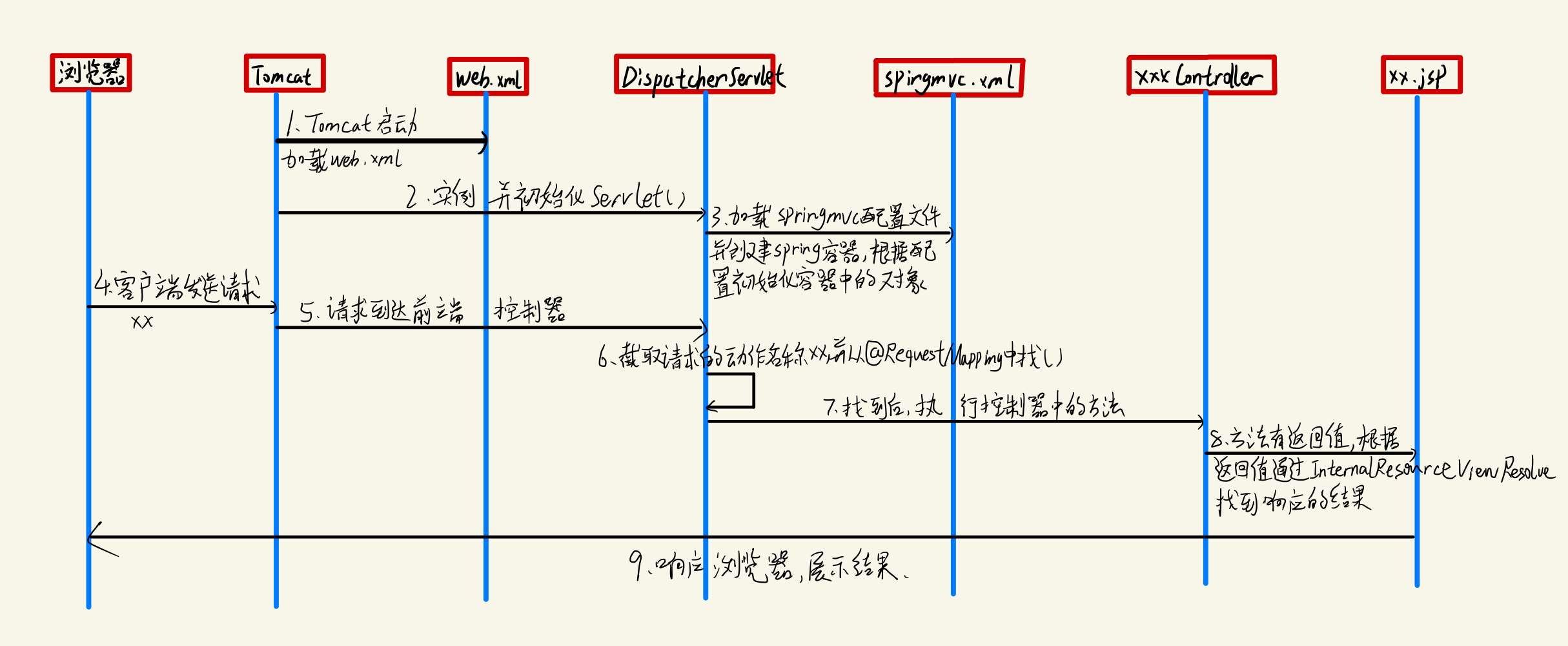
3.2 执行逻辑
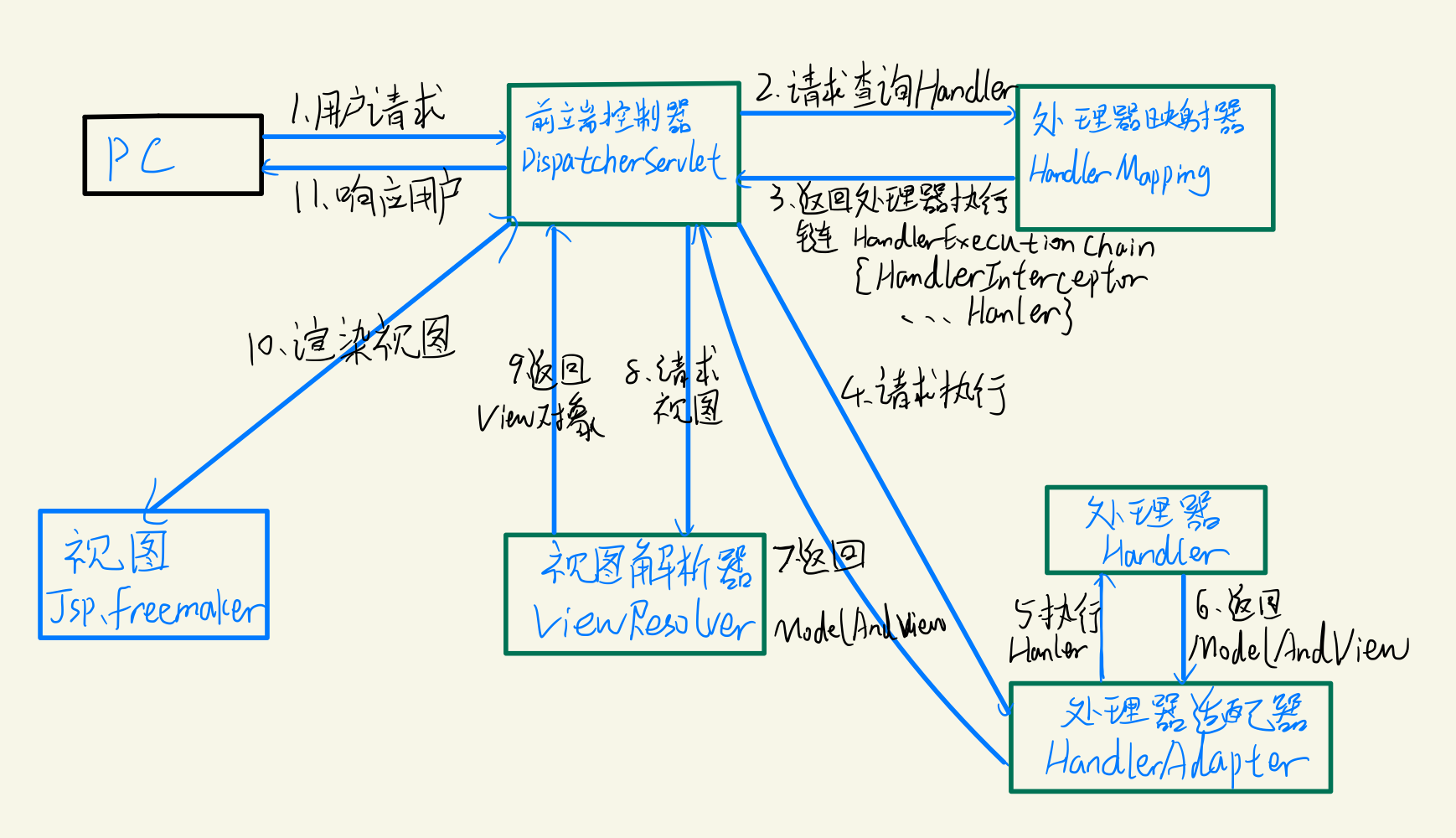
DispatcherServlet:前端控制器
- 用户请求到达前端控制器,它就相当于 mvc 模式中的 c,dispatcherServlet 是整个流程控制的中心,由 它调用其它组件处理用户的请求,dispatcherServlet 的存在降低了组件之间的耦合性。
HandlerMapping:处理器映射器(三大组件)- HandlerMapping 负责根据用户请求找到 Handler 即处理器,SpringMVC 提供了不同的映射器实现不同的 映射方式,例如:配置文件方式,实现接口方式,注解方式等。
Handler:处理器 (自己定义的Controller处理单元)
- 它就是我们开发中要编写的具体业务控制器。由 DispatcherServlet 把用户请求转发到 Handler。由 Handler 对具体的用户请求进行处理。
HandlAdapter:处理器适配器(三大组件)- 通过 HandlerAdapter 对处理器进行执行,这是适配器模式的应用,通过扩展适配器可以对更多类型的处理器进行执行
View Resolver:视图解析器(三大组件)- View Resolver 负责将处理结果生成 View 视图,View Resolver 首先根据逻辑视图名解析成物理视图名 即具体的页面地址,再生成 View 视图对象,最后对 View 进行渲染将处理结果通过页面展示给用户。
View:视图- SpringMVC 框架提供了很多的 View 视图类型的支持,包括:jstlView、freemarkerView、pdfView等。我们最常用的视图就是 jsp。 一般情况下需要通过页面标签或页面模版技术将模型数据通过页面展示给用户,需要由程序员根据业务需求开 发具体的页面。
<mvc:annotation-driven>说明- 在 SpringMVC 的各个组件中,
处理器映射器、处理器适配器、视图解析器称为 SpringMVC 的三大组件。 - 使 用
<mvc:annotation-driven>自动加载 RequestMappingHandlerMapping (处理映射器) 和 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter ( 处 理 适 配 器 ) , 可 用 在 SpringMVC.xml 配 置 文 件 中 使 用<mvc:annotation-driven>替代注解处理器和适配器的配置
- 在 SpringMVC 的各个组件中,
<!--开启MVC注解驱动,自动配置处理器映射器与适配器-->
<mvc:annotation-driven />
<!--配置处理器映射器-->
<!--
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping"/>
-->
<!--配置处理器适配器-->
<!--
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter"/>
-->开启
<mvc:annotation-driven />后,自动配置处理器映射器与适配器当配置了mvc:annotation-driven/后,Spring就知道了我们启用注解驱动。然后Spring通过context:component-scan/标签的配置,会自动为我们将扫描到的@Component,@Controller,@Service,@Repository等注解标记的组件注册到工厂中,来处理我们的请求,这个时候接收返回json数据、参数验证、统一异常等功能
3.2.1 静态资源放行
静态资源:类似于js或者css等类型的文件,保持不变的资源静态资源放行:服务器在遇到请求静态资源时,不匹配对应的 controller,而直接放行请求去对应路径找相关文件配置静态资源放行mapping:映射的 url 路径(浏览器请求的 url)location:需要映射的静态资源所在目录地址- 在
springmvc.xml中配置以下内容
<!--静态资源放行-->
<mvc:resources mapping="/js/**" location="/js/"></mvc:resources>
<mvc:resources mapping="/img/**" location="/img/"></mvc:resources>
<mvc:resources mapping="/css/**" location="/css/"></mvc:resources>4 控制请求方式
4.1 @RequestMapping控制请求方式
- method属性可以控制请求的方式,值为RequestMethod的枚举值
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/mikevane")
public class MyController {
@RequestMapping(value = "firstController", method = {RequestMethod.GET})
public String firstController(){
System.out.println("firstController");
return "first";
}
}4.2 @RequestMapping控制请求参数params和请求头headers
param:表示请求中必须包含名为param的参数!param:表示请求中不能包含名为param的参数param = value:表示请求中包含名为param的参数,但是值必须是valueparam != value:表示请求中包含名为param的参数,但是值不能是value{"param1","param2=value"}:可以将对于多个参数的要求写入数组
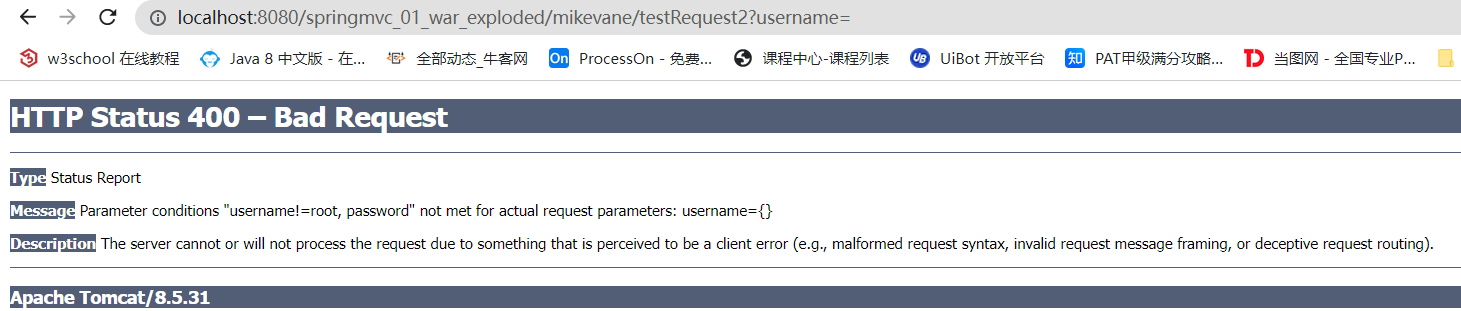
@RequestMapping(value = "/testRequest2", params = {"username!=root","password"})
public String testRequest2(){
System.out.println("testRequest2");
return "success";
}
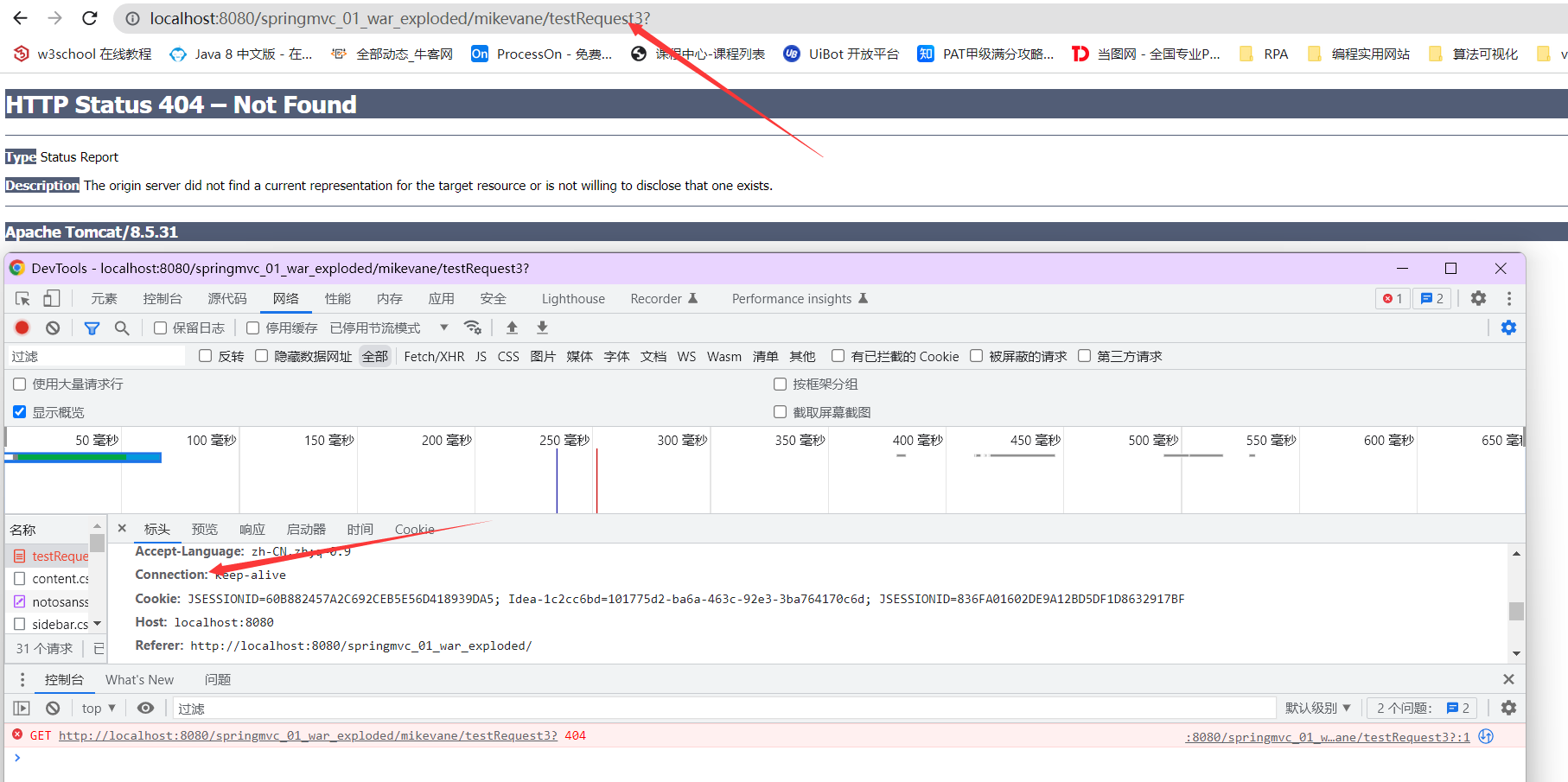
@RequestMapping(value = "/testRequest3", headers = {"!Connection"})
public String testRequest3(){
System.out.println("testRequest3");
return "success";
}- 如果访问
testRequest2,url中没有 password,那么就会出现报错 - 如果访问
testRequest3,请求头出现了 Connection,则也会出现报错
4.3 @PathVariable注解和RESTful风格的支持
普通形式的url- *****/contextPath/aaa.do
- *****/contextPath/aaa.jsp
- *****/contextPath/aaa.html
- *****/contextPath/css/aaa.css
- *****/contextPath/js/aaa.js
- *****/contextPath/aaa.do?id=10&username=root
restFul风格的url- *****/contextPath/aaa/10/root
- *****/contextPath/aaa
示例:测试restFul风格的urlcontroller层
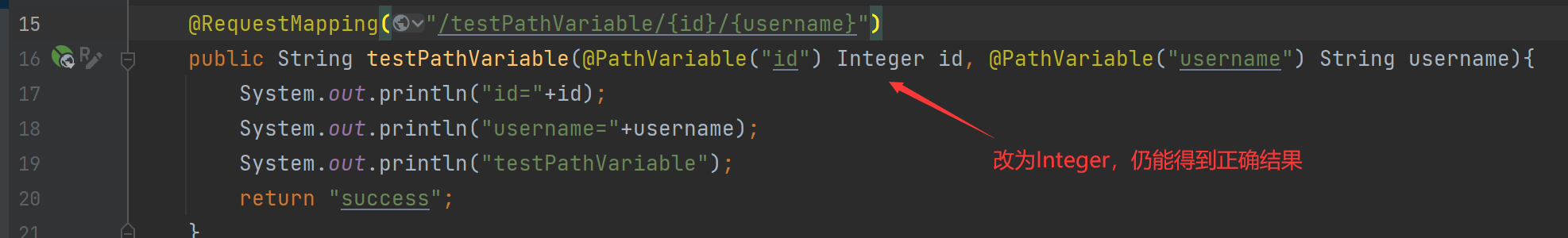
@RequestMapping("/testPathVariable/{id}/{username}")
public String testPathVariable(@PathVariable("id") String id, @PathVariable("username") String username){
System.out.println("id="+id);
System.out.println("username="+username);
System.out.println("testPathVariable");
return "success";
}这里的访问路径为:
***/testPathVariable/{id}/{username}注意:@PathVariable里面的 value 值要与@RequestMapping里对应大括号的变量名一致(比如id或者username)- 方法的
形参名可随意取,这里的形参名与请求参数的变量名一致只是因为可读性更强
这里还可以把形参类型改为
Integer,框架会自动进行类型识别与转换
RESTFUL- 是一种网络应用程序的设计风格和开发方式,基于HTTP,可以使用
XML格式定义或JSON格式定义 - 适用于移动互联网厂商作为业务接口的场景,实现第三方
OTT调用移动网络资源的功能,动作类型为新增、变更、删除所调用资源
- 是一种网络应用程序的设计风格和开发方式,基于HTTP,可以使用
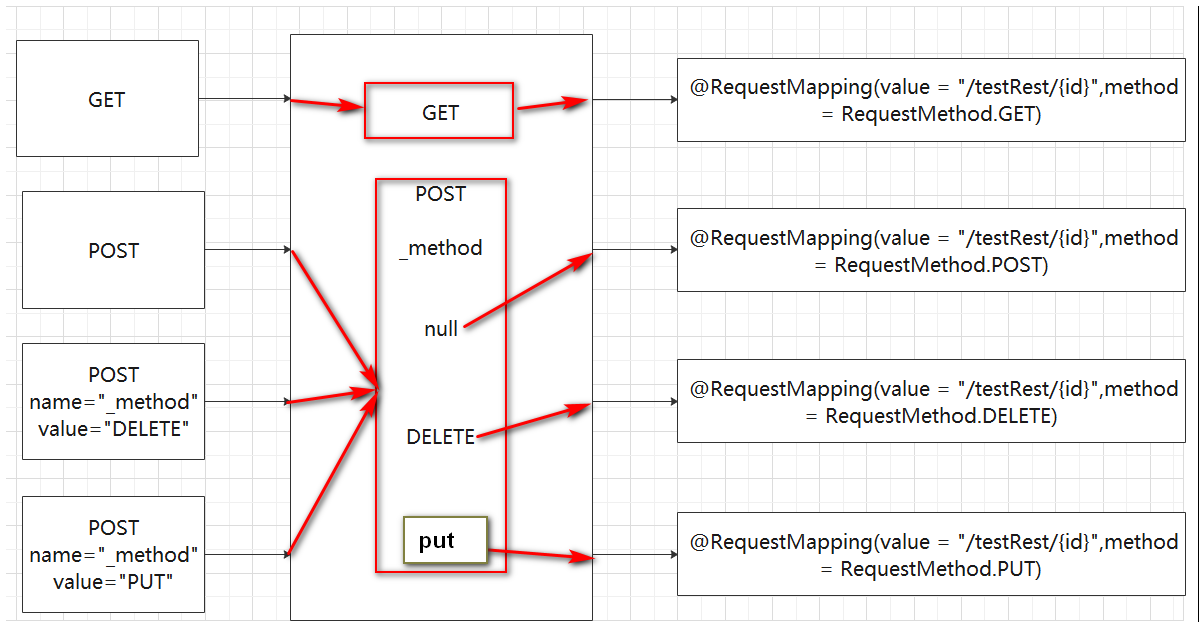
ESTFUL特点包括:- 每一个URI代表1种资源;
- 客户端使用GET、POST、PUT、DELETE4个表示操作方式的动词对服务端资源进行操作:GET用来获取资源,POST用来新建资源(也可以用于更新资源),PUT用来更新资源,DELETE用来删除资源;
- 通过操作资源的表现形式来操作资源;
- 资源的表现形式是XML或者HTML;
- 客户端与服务端之间的交互在请求之间是无状态的,从客户端到服务端的每个请求都必须包含理解请求所必需的信息
针对上述的第二个特点进行拓展:- 简单的说,就是我们在访问资源时,可以通过这四个状态来表示对于资源的不同操作,这四个状态表现为我们请求的四种方式
- /controller/1 HTTP GET :得到id为1 的资源
- /controller/1 HTTP DELETE :删除id为1的资源
- /controller/1 HTTP PUT :更新id为1 的资源
- /controller/1 HTTP POST :增加id为1 的资源
- 更简单地说:在访问同一个url的时候,通过不同的请求方式,对应到不同的controller处理单元
测试不同请求方式GET与POST Controller代码
@RequestMapping(value = "testRestful/{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String testGET(@PathVariable("id") String id){
System.out.println("testGet");
System.out.println("id="+id);
return "success";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "testRestful/{id}",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String testPOST(@PathVariable("id") String id){
System.out.println("testPOST");
System.out.println("id="+id);
return "success";
}GET和POST jsp代码
<form action="testRestful/10" method="get">
<input type="submit" name="getButton">
</form>
<br/>
<form action="testRestful/10" method="post">
<input type="submit" name="getButton">
</form>PUT与DELETE Controller层代码
@RestController
public class TestRestFul {
@RequestMapping(value = "testRestful/{id}",method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public String testPUT(@PathVariable("id") String id){
System.out.println("testPUT");
System.out.println("id="+id);
return "success";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "testRestful/{id}",method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public String testDELETE(@PathVariable("id") String id){
System.out.println("testDELETE");
System.out.println("id="+id);
return "success";
}
}- 因为
form标签中的method属性不提供PUT或DELETE,所以需要使用其他方法来转化POST请求- 在
form标签中加入:<input type=”hidden” name=”_method” value=”DELETE”> - 将
Controller改为RestController,这样返回的字符串,浏览器就可以作为字符串处理,而不是资源 - 在
web.xml中配置请求过滤器(hiddenHttpMethodFilter)
- 在
<!--配置hiddenHttpMethodFilter ,将POST请求转换为PUT或者DELETE请求-->
<filter>
<filter-name>hiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>hiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>PUT与DELETE JSP代码
<form action="testRestful/10" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="PUT">
<input type="submit" name="getButton">
</form>
<form action="testRestful/10" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="DELETE">
<input type="submit" name="getButton">
</form>- 测试点击对应的按钮,控制台返回结果为:
testPUT
id=10
testDELETE
id=10- 说明对PUT和DELETE的处理成功
5 获取请求参数
5.1 紧耦合方式参数注入(了解)
紧耦合方式参数注入- 使用传统的HTTPServletRequest对象获取参数
- 需要导入jar包:javax.servlet
controller层代码
@RequestMapping("/getParamByRequest")
public String getParam1(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response){
String username = request.getParameter("username");
String password = request.getParameter("password");
System.out.println("username:"+username+" password:"+password);
return "getParamSuccess";
}jsp代码
<form action="getParamByRequest" method="get">
<input type="text" name="username">
<input type="password" name="password">
<input type="submit" name="paramSubmit">
</form>5.2 松耦合方式参数注入
松耦合方式参数注入- 不使用传统的HTTPServletRequest对象获取参数
- 通过SpringMVC的框架功能,
自动转换参数 - 不需要导入额外jar包
注意:- 如果在形参
不加入任何注解的情况下,处理单元参数列表中的参数名要与请求中的参数名一致 - 可以使用
@RequestParam来进行指定对应的参数名,这时候处理单元参数的参数名可以与请求的参数名不一致 - 框架可以进行
类型自动转换,比如接收的参数类型是Integer,那么处理器适配器会将接收到的数据进行数据类型转换
- 如果在形参
controller层
@RequestMapping("/getParamByArgName")
public String getParam2(String username, @RequestParam("pwd") String password){
System.out.println("username:"+username+" password:"+password);
return "getParamSuccess";
}jsp代码
<form action="getParamByArgName" method="get">
<input type="text" name="username">
<input type="password" name="pwd">
<input type="submit" name="paramSubmit">
</form>5.3 POJO接收参数
使用POJO接收参的注意事项- 提交的参数名必须和POJO的属性名保持一致(假如提交的name为pname,那么实体类中属性的名字也要为pname才能接收数据)
- springmvc底层通过
反射给参数列表的属性赋值(处理器适配器会自动从Request中解析数据) - 通过
set方法设置属性值的,不是直接通过操作属性 - POJO的属性一定要有set方法,要不然就会接收失败
示例:pojo代码
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Data
public class Person implements Serializable {
private String pname;
private String page;
private String gender;
private String[] hobby;
private Date birthdate;
}controller层代码
@RequestMapping("/getDataByPojo")
public String getDataByPojo(Person p){
System.out.println(p);
return "success";
}JSP代码
<form action="getDataByPojo" method="post">
<p>姓名<input type="text" name="pname"></p>
<p>年龄<input type="text" name="page"></p>
<p>性别:
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="1" >男
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="0" >女
</p>
<p>爱好
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="1"> 篮球
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="2"> 足球
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="3"> 羽毛球
</p>生日
<p>
<input type="text" name="birthdate">
</p>
<input type="submit">
</form>5.4 日期类型转换
5.4.1 注解方式(推荐)
@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd"):可以用于方法参数列表和类的属性上@DateTimeFormat 用于类的属性pojo代码
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Data
public class Person implements Serializable {
private String pname;
private String page;
private String gender;
private String[] hobby;
@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd")
private Date birthdate;
}
controller代码
@RequestMapping("/getDataByPojo")
public String getDataByPojo(Person p){
System.out.println(p);
return "success";
}@DateTimeFormat 用于 方法参数列表
@RequestMapping("/getDataByPojo")
public String getDataByPojo(@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd") Date birthdate){
System.out.println(birthdate);
return "success";
}5.4.2 配置转换器
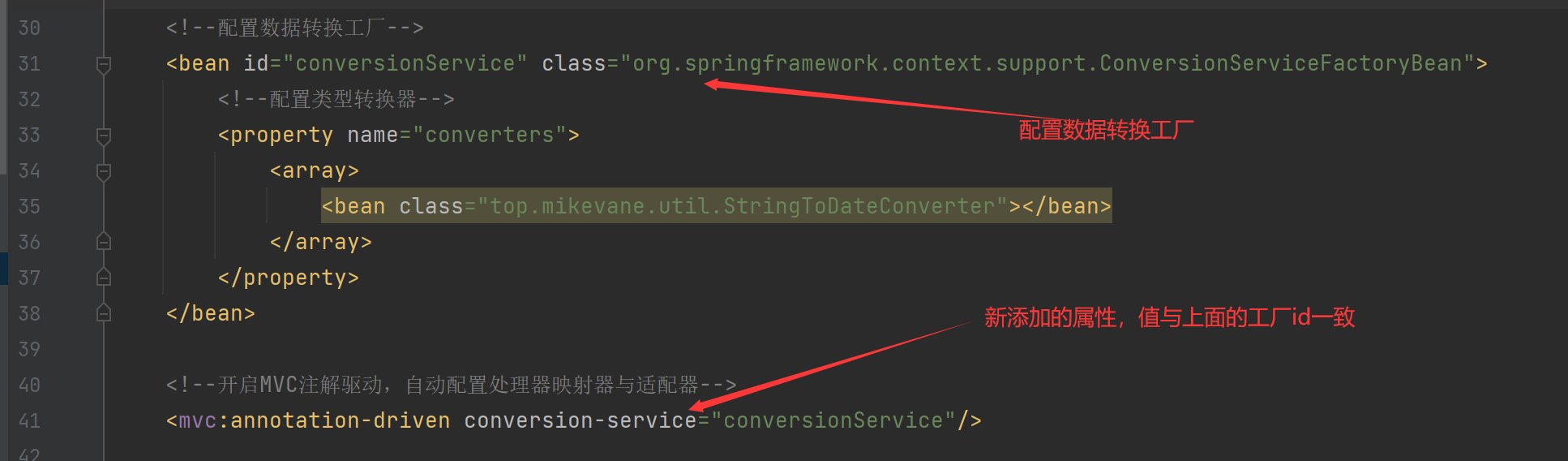
- 告诉 springmvc 在遇到 ``String类转为Date类` 的时候,使用 类型转换器
实现步骤
- 新建类,实现
Converter接口
public class StringToDateConverter implements Converter<String, Date> {
private SimpleDateFormat dateFormat=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
@Override
public Date convert(String source) {
Date date =null;
try {
date = dateFormat.parse(source);
} catch (ParseException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("日期转换异常");
}
return date;
}
}- 在
springmvc.xml中配置数据转换工厂
5.5 List集合接收参数
注入单独的对象逻辑同
List集合接收参数,后面不再多阐述因为 springmvc 支持的问题,List参数不能直接放到方法参数列表
- 将List对应的对象作为
另一个类的属性进行传入 - 利用
Ajax + JSON进行传入
- 将List对应的对象作为
这里
使用第一种方式进行解决pojo代码
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Data
public class Person implements Serializable {
private String pname;
private String page;
private String gender;
private String[] hobby;
@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd")
private Date birthdate;
private List<Pet> pets;
}Controller层代码
@RequestMapping("/getDataByPojo")
public String getDataByPojo(Person p){
System.out.println(p);
System.out.println(p.getPets());
return "success";
}JSP代码(仅书写List相关的代码)
宠物List:
<p>
宠物1: 名字:<input type="text" name="pets[0].petName" >类型:<input type="text" name="pets[0].petType">
</p>
<p>
宠物2: 名字:<input type="text" name="pets[1].petName" >类型:<input type="text" name="pets[1].petType">
</p>测试输入

- 控制台显示:
Person(pname=asd, page=10, gender=null, hobby=[1, 2], birthdate=Tue Sep 21 00:00:00 CST 1999, pets=[Pet(petName=tom, petType=cat), Pet(petName=jerry, petType=mouse)])
[Pet(petName=tom, petType=cat), Pet(petName=jerry, petType=mouse)]- 结果显示正确
5.6 Map集合接收参数
pojo代码:加入类型为map的属性
//这里的String对应后面jsp中name中petMap的key类型
private Map<String,Pet> petMap;Controller层
@RequestMapping("/getDataByPojo")
public String getDataByPojo(Person p){
System.out.println(p.getPetMap());
return "success";
}JSP代码:注意,这里的name中的 petMap 的 key 可以任意取值(这里取值a和b只是为了测试)
宠物Map:
<p>
宠物1: 名字:<input type="text" name="petMap['a'].petName" >类型:<input type="text" name="petMap['a'].petType">
</p>
<p>
宠物2: 名字:<input type="text" name="petMap['b'].petName" >类型:<input type="text" name="petMap['b'].petType">
</p>5.7 请求参数中文乱码问题
5.7.1 GET乱码问题
- 在
tomcat根目录/conf/server.xml中的 <Connector> 标签上加入属性URIEncoding="utf-8"
<Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
connectionTimeout="20000"
redirectPort="8443" URIEncoding="utf-8"/>5.7.2 POST乱码问题
因为 POST 方式数据是单独打包的
在
web.xml中配置编码过滤器
<!--Spring 中提供的字符编码过滤器-->
<filter>
<filter-name>encFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>utf-8</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>encFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>6 常见注解
6.1 @RequestMapping
作用:- 用于建立请求 URL 和处理请求方法之间的对应关系
出现位置:类上:请求 URL 的第一级访问目录。此处不写的话,就相当于应用的根目录。写的话需要以/开头方法上: 请求 URL 的第二级访问目录
属性:value:用于指定请求的 URL。它和 path 属性的作用是一样的。method:用于指定请求的方式。params(了解):用于指定限制请求参数的条件。它支持简单的表达式。要求请求参数的 key 和 value 必须和 配置的一模一样。headers(了解):用于指定限制请求消息头的条件
6.2 @RequestParam
作用:- 把请求中指定名称的参数给控制器中的形参赋值。
属性:value:请求参数中的名称。required:请求参数中是否必须提供此参数。默认值:true。表示必须提供,如果不提供将报错。
@RequestMapping("/getRequestParam")
public String getRequestParam(@RequestParam("name")String uname, @RequestParam(value="age",required=false)Integer age){
System.out.println(username+","+age);
return "success";
}6.3 @PathVariable
Restful的简介:- REST(英文:Representational State Transfer,简称 REST)restful是一种软件架构风格、设计风格,而不是标准,只是提供了一组设计原则和约束条件。它主要用于客户端和服务器交互类的软件。基于这个风格设计的软件可以更简洁,更有层次,更易于实现缓存等机制。
Restful的优点- 它结构清晰、符合标准、易于理解、扩展方便,所以正得到越来越多网站的采用。
作用:- 用于绑定 url 中的占位符。例如:请求 url 中 /delete/{id},这个{id}就是 url 占位符。 url 支持占位符是 spring3.0 之后加入的。是 springmvc 支持 rest 风格 URL 的一个重要标志。
属性:- value:用于指定 url 中占位符名称。
- required:是否必须提供占位符。
@RequestMapping("/testPathVariable/{id}/{username}")
public String testPathVariable(@PathVariable("id") Integer id, @PathVariable("username") String username){
System.out.println("id:"+id);
System.out.println("username:"+username);
System.out.println("testPathVariable1");
return "success";
}
6.4 @RequestHeader(了解)
作用:- 用于获取请求消息头。
属性:value:提供消息头名称required:是否必须有此消息头
@RequestMapping("/getRequestHeader")
public String getRequestHeader(@RequestHeader(value="Accept", required=false)String requestHeader){
System.out.println(requestHeader);
return "success";
}6.5 @CookieValue(了解)
作用:- 用于把指定 cookie 名称的值传入控制器方法参数。
属性:value:指定 cookie 的名称。required:是否必须有此 cookie
@RequestMapping("/getCookie")
public String getCookie(@CookieValue(value="JSESSIONID",required=false) String cookieValue){
System.out.println(cookieValue);
return "success";
} 7 响应处理
- 以前我们是自己在Servlet中使用response对象来完成响应的,那么在SpringMVC中如何响应请求的处理结果呢?
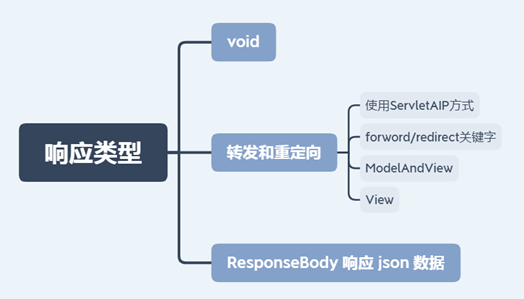
7.1 单元方法返回值为void
例子:如果按照之前的方法,直接返回void
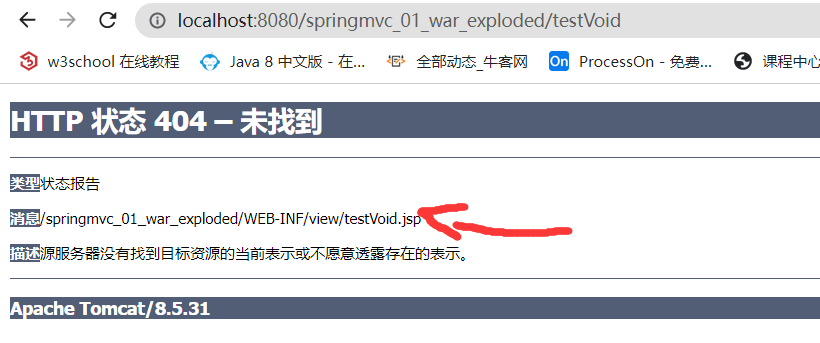
@RequestMapping("testVoid")
public void testVoid(){
System.out.println("void controller");
}- 在浏览器访问相应的地址后会发现,框架会自动去找和自己控制单元名称一致的页面展示 (
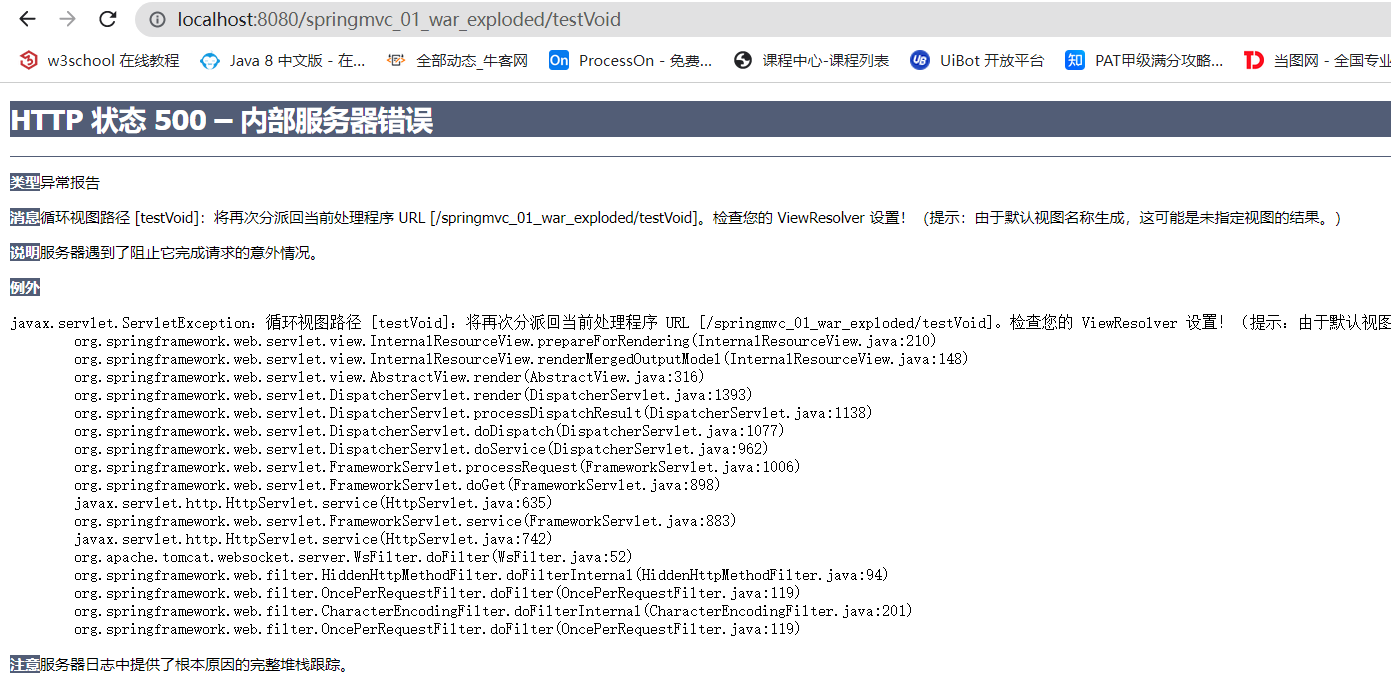
testVoid.jsp)(这里是因为配置了视图解析器才造成了404),但其实我只是想返回 void - 关闭了对应的
视图解析器,重新访问该地址仍然会出现错误,但是这次错误为500
7.2 转发和重定向
7.2.1 紧耦合方式(了解)
重定向的特点:redirect- 地址栏发生变化
- 重定向可以访问其他站点(服务器)的资源
- 重定向是两次请求,不能使用request对象来共享数据
转发的特点:forward- 转发地址栏路径不变
- 转发只能访问当前服务器下的资源
- 转发是一次请求,可以使用request对象来共享数据
请求转发
@RequestMapping("demo1")
public void testDemo1(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// 请求转发
request.getRequestDispatcher("/forwardPage.jsp").forward(request,response);
}相应重定向
@RequestMapping("demo1")
public void testDemo1(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// 响应重定向
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath()+"/redirectPage.jsp");
}- 单元方法的返回值类型设置void。因为使用response对象在单元方法中直接对此次请求进行了响应,不再通过DispatcherServlet了,既然已经响应了,就不需要再给DispatcherServlet返回值了。在单元方法上声明HttpServletResponse形参,来接收此次请求的response对象
7.2.2 forward关键字
forward: 关键字,就是请求转发注意- 返回字符串告诉
DispatcherServlet跳转的路径
- 在路径之前放上一个
forward
- 如果路径前的关键字是forward,那么
可以省略不写(即下面的forward可以省略)
- 返回字符串告诉
@RequestMapping("demo2")
public String testDemo2(){
//return "forward:/forwardPage.jsp";
return "/forwardPage.jsp";
}7.2.3 redirect关键字
redirect:关键字,就是重定向注意- 返回字符串告诉
DispatcherServlet跳转的路径
- 在路径之前放上一个redirect
- 如果路径前的关键字是redirect,那么
不可以省略 /表示当前项目下.这里不需要项目的上下文路径
- 返回字符串告诉
@RequestMapping("demo3")
public String testDemo3(){
return "redirect:/redirectPage.jsp";
}7.2.4 View视图转发和重定向
请求转发
@RequestMapping("demo4")
public View testDemo4(){
//请求转发
View view = new InternalResourceView("/forwardPage.jsp");
return view;
}重定向
@RequestMapping("demo4")
public View testDemo4(){
//重定向
View view = new RedirectView("redirectPage.jsp");
return view;
}- RedirectView中所做的操作,最终的实现是在renderMergedOutputModel中完成实现的,简单来说RedirectView实现了链接的重定向,并且将数据保存到FlashMap中,这样在跳转后的链接中可以获取一些数据
7.2.5 ModelAndView转发重定向
请求转发
@RequestMapping("demo5")
public ModelAndView testDemo5(){
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
//请求转发
//modelAndView.setViewName("forward:/forwardPage.jsp");
modelAndView.setView(new InternalResourceView("forwardPage.jsp"));
return modelAndView;
}重定向
@RequestMapping("demo5")
public ModelAndView testDemo5() {
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
// modelAndView.setViewName("redirect:/redirectPage.jsp");
modelAndView.setView(new RedirectView("redirectPage.jsp"));
return modelAndView;
}ModelAndView中的Model代表模型,View代表视图,这个名字就很好地解释了该类的作用业务处理器调用模型层处理完用户请求后,把结果数据存储在该类的 model 属性中,把要返回的视图信息存储在该类的 view 属性中,然后让该ModelAndView返回该Spring MVC框架
7.2.6 @ResponseBody 响应 json 数据
为什么使用@ResponseBody- 当浏览器发起一个ajax请求给服务器,服务器调用对应的单元方法处理ajax请求。而ajax的请求在被处理完成后,其处理结果需要直接响应。而目前我们在单元方法中响应ajax请求,使用的是response对象,需要我们自己将要响应的数据转换为json字符串响应,比较麻烦,而
我们一直希望在单元方法中无论是否是ajax请求,都使用return语句来完成资源的响应,怎么办? - 既然我们希望使用单元方法的返回值来响应ajax请求的处理结果,而目前DispatcherServlet的底层会将单元方法的返回值按照请求转发或者重定向来处理,
所以就需要我们告诉DispatcherServlet,单元方法的返回值不要按照请求转发或者重定向处理,而是按照直接响应处理,将单元方法的返回值直接响应给浏览器
- 当浏览器发起一个ajax请求给服务器,服务器调用对应的单元方法处理ajax请求。而ajax的请求在被处理完成后,其处理结果需要直接响应。而目前我们在单元方法中响应ajax请求,使用的是response对象,需要我们自己将要响应的数据转换为json字符串响应,比较麻烦,而
@ResponseBody的作用- 方法的返回值不再作为界面跳转依据,而是直接作为返回的数据
- 将方法的返回的数据
自动使用ObjectMapper转换为JSON
导入jackson的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.12.1</version>
</dependency>- 声明单元方法处理ajax请求,并在单元方法上
新增注解@ResponseBody(Person对象是为了接收前端传的数据)
@RequestMapping("testAjax")
public Pet testAjax(Person p) throws JsonProcessingException {
System.out.println(p);
Pet pet =new Pet("Tom","cat");
return pet;
}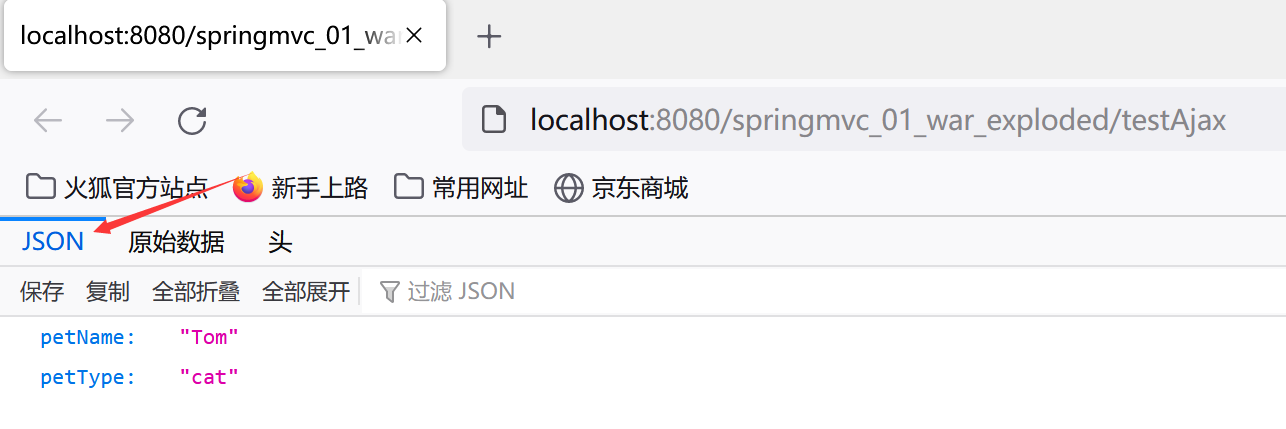
- 在ajax的回调函数中,
无需再次使用eval函数将响应数据转换为json对象,直接使用即可
<script>
$(function () {
$("#btn").click(function () {
$.get('testAjax',{pname:"mikevane",page:"18"},function(data){
console.log(data.petName)
console.log(data.petType)
})
})
})
</script>
<body>
<input id="btn" type="button" value="testJSON">
</body>
关于 @RestController
- 相当于@Controller+@ResponseBody两个注解的结合,返回json数据不需要在方法前面加@ResponseBody注解了,但使用@RestController这个注解,就不能返回jsp.html页面,视图解析器无法解析jsp.html页面
8 SSM整合
8.1 准备数据库
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`uid` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`uname` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`password` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`uid`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=3 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;8.2 创建maven web项目并补充项目结构
8.3 更新web.xml 文件和准备包结构
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
</web-app>
8.4 导入依赖
<dependencies>
<!--spring核心容器包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.5</version>
</dependency>
<!--spring切面包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>5.3.5</version>
</dependency>
<!--aop联盟包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>aopalliance</groupId>
<artifactId>aopalliance</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
</dependency>
<!--德鲁伊连接池-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql驱动-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.22</version>
</dependency>
<!--springJDBC包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.5</version>
</dependency>
<!--spring事务控制包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>5.3.5</version>
</dependency>
<!--spring orm 映射依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-orm</artifactId>
<version>5.3.5</version>
</dependency>
<!--Apache Commons日志包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-logging</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
<!--log4j2 日志-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-slf4j-impl</artifactId>
<version>2.14.0</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--lombok -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.12</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!--spring test测试支持包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.3.5</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--junit5单元测试-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId>
<version>5.7.0</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--springMVC支持包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>5.3.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.5</version>
</dependency>
<!--jsp 和Servlet 可选-->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet.jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.3.3</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!--json依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.12.1</version>
</dependency>
<!--mybatis 核心jar包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.3</version>
</dependency>
<!--spring mybatis整合包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>2.0.3</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>8.5 log4j2.xml配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Configuration status="DEBUG">
<Appenders>
<Console name="Console" target="SYSTEM_ERR">
<PatternLayout pattern="%d{YYYY-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} [%t] %-5p %c{1}:%L - %msg%n" />
</Console>
</Appenders>
<Loggers>
<Root level="DEBUG">
<AppenderRef ref="Console" />
</Root>
</Loggers>
</Configuration>8.6 jdbc.properties配置
jdbc_driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jdbc_url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mydb?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
jdbc_username=root
jdbc_password=1234568.7 springMVC.xml配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
">
<!--扫描controller-->
<context:component-scan base-package="top.mikevane.controller"></context:component-scan>
<!--这里配置三大组件-->
<mvc:annotation-driven />
<!--视图解析器-->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
</bean>
<!--配置静态资源放行-->
<!--<mvc:resources mapping="/js/**" location="/js/"></mvc:resources>-->
<!--<mvc:resources mapping="/css/**" location="/css/"></mvc:resources>-->
<!--<mvc:resources mapping="/img/**" location="/img/"></mvc:resources>-->
<!--<mvc:resources mapping="/static/**" location="/static/"></mvc:resources>-->
</beans>8.8 applicationContext.xml配置
- spring整合MyBatis思路:
- 目的是
在Service层注入Mapper对象 - Mapper对象是由MyBatis生成(使用了SqlSession.getMapper(xxxMapper.class))
- MyBatis生成Mapper对象过程:
SqlSessionFactory -> SqlSession -> mapper - 所以可以使用 spring 来创建 SqlSessionFactory 与 SqlSession 对象,然后再使用 spring 创建 mapper
- 目的是
<!--加载properties配置文件-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath*:jdbc.properties"/>
<!--包扫描,仅仅扫描Service层-->
<context:component-scan base-package="top.mikevane.service"/>
<!--配置数据源-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc_driver}"></property>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc_url}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc_username}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc_password}"></property>
</bean>
<!--SqlSessionFactoryBean(spring整合包里的)-->
<bean id="factory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<!--配置数据源-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
<!--实体类别名包扫描-->
<property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="top.mikevane.pojo"></property>
</bean>
<!--MapperScanner mapper扫描仪(生成所有Mapper对象并放入容器中)-->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<!--注入SqlSessionFactory-->
<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="factory"></property>
<!--读取所有Mapper映射文件-->
<property name="basePackage" value="top.mikevane.mapper"></property>
</bean>
<!--事务管理器-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--开启事务注解-->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"></tx:annotation-driven>8.9 web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<!--spring核心配置文件位置-->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!--spring Listener-->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<!--DispatcherServlet-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath*:springmvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<!--编码过滤器-->
<filter>
<filter-name>characterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>UTF-8</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>characterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
</web-app>8.10 开发业务代码
index.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="login" method="post">
<input type="text" name="username">
<input type="text" name="password">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>success.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
登录成功
</body>
</html>fail.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
登录失败
</body>
</html>User POJO
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class User implements Serializable {
private int uid;
private String uname;
private String password;
}
UserController
@Controller
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@RequestMapping(value = "login",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String login(@RequestParam("username") String username, @RequestParam("password") String password){
String view = "";
User user = userService.findUser(username,password);
if(user == null){
view = "fail.jsp";
} else {
view = "success.jsp";
}
return view;
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("findAllUser.do")
public List<User> findAllUser(){
return userService.findAllUser();
}
}UserService
@Service
@Transactional
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
/**
* 根据用户名与密码查询对应的用户
* @param username
* @param password
* @return 存在返回用户对象,不存在返回null
*/
public User findUser(String username, String password) {
return userMapper.findUser(username,password);
}
/**
* 查找所有User对象
* @return
*/
public List<User> findAllUser() {
return userMapper.findAllUser();
}
}UserMapper
public interface UserMapper {
User findUser(@Param("username") String username, @Param("password") String password);
List<User> findAllUser();
}UserMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="top.mikevane.mapper.UserMapper">
<!--User findUser(String uname, String password);-->
<select id="findUser" resultType="user">
select * from user where uname =#{username} and password =#{password}
</select>
<!--findAllUser-->
<select id="findAllUser" resultType="user">
select * from user
</select>
</mapper>9 作用域传参
| 名称 | 作用域 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| PageContext | 当前jsp页面内有效 | |
| request | 一次请求内 | 解决了一次请求内的资源的数据共享问题 |
| session | 一次会话内有效 说明:浏览器不关闭,并且后台的session不失效,在任意请求中都可以获取到同一个session对象 |
解决了一个用户不同请求的数据共享问题 |
| application(ServletContext) | 整个项目内有效 | 解决了不同用户的数据共享问题 |
9.1 传统方式传递数据
- request,session 这两个域
直接放在参数列表上即可,SpringMVC就可以给我们注入 - ServletContext对象(application域) 不能直接放在参数列表上的,需要通过HttpServletRequest获取
示例三个域的使用Controller
@Controller
public class ScopeController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@RequestMapping("setData")
public String setData(HttpServletRequest req, HttpSession session){
List<User> users = userService.findAllUser();
// 向三个域中放入数据
req.setAttribute("message", "reqMessage");
req.setAttribute("users", users);
session.setAttribute("message", "sesssionMessage");
session.setAttribute("users", users);
ServletContext application = req.getServletContext();
application.setAttribute("message", "applictionMessage");
application.setAttribute("users", users);
// 跳转至showDataPage
return "/showDataPage.jsp";
}
}showDataPage.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%--域中的数据--%>
requestScope :message:${requestScope.message} ,uname:${requestScope.users[0].uname} <br/>
sessionScope :message:${sessionScope.message} ,uname:${sessionScope.users[0].uname} <br/>
applicationScope :message:${applicationScope.message} ,uname:${applicationScope.users[0].uname} <br/>
<%--请求参数--%>
requestParam:${param.message}
</body>
</html>9.2 Model传递数据(针对请求域)
Model对象- 主要是对
请求域(Request)传递数据进行了API上的封装 - 降低controller和Servlet之间的
耦合度 - 如果使用
重定向,则没法使用model传递域中的数据- 但是
使用重定向,model中的字符串类型的键值对信息会转换为请求参数,转发给目标组件 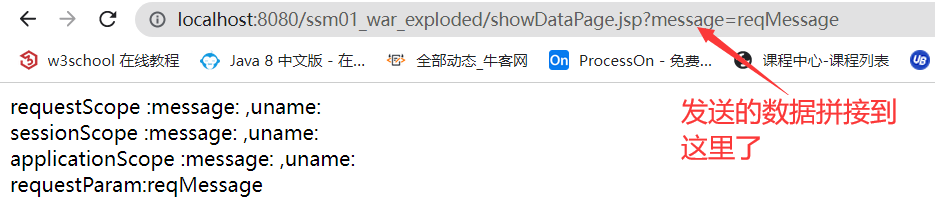
- 但是
- 主要是对
@RequestMapping("setData2")
public String setData2(Model model){
List<User> users = userService.findAllUser();
// 向域中放入数据
model.addAttribute("message", "reqMessage");
model.addAttribute("users", users);
// 跳转至showDataPage
return "forward:/showDataPage.jsp";
//return "redirect:/showDataPage.jsp";
}9.3 ModelAndView传递数据(针对请求域)
ModelAndViewModel:理解为数据View:理解为页面- 如果使用
重定向,与Model传递数据的情况一模一样
@RequestMapping("setData3")
public ModelAndView setData3(){
ModelAndView mv=new ModelAndView();
Map<String, Object> model = mv.getModel();
// 向request域中放入数据
List<User> users = userService.findAllUser();
model.put("message", "reqMessage");
model.put("users", users);
// 设置视图
mv.setViewName("forward:/showDataPage.jsp");
//mv.setViewName("redirect:/showDataPage.jsp");
return mv;
}10 上传
需求:- 游戏用户注册功能
- 输入账号密码与昵称
- 设置头像(异步)
- 点击浏览,选择磁盘中的文件
- 点击立即上传,上传成功会在页面上显示选择的图片,上传失败会出现提示
- 注册后,上面的数据存入数据库中
实现中遇到的问题如何在页面中显示一个按钮- 用户可以点击该按钮后选择本地要上传的文件在页面中使用
input标签,type值设置为”file”即可
- 用户可以点击该按钮后选择本地要上传的文件在页面中使用
确定上传请求的发送方式- 上传成功后的响应结果在
当前页面显示,使用ajax请求来完成资源的发送
- 上传成功后的响应结果在
上传请求的请求数据及其数据格式请求数据:- 上传的文件本身普通数据:用户名,Id,密码等,
建议上传功能中不携带除上传资源以外的数据
- 上传的文件本身普通数据:用户名,Id,密码等,
数据格式:传统的请求中,请求数据是以键值对的格式来发送给后台服务器的,但是在上传请求中,没有任何一个键可以描述上次的数据,因为数据本身是非常大的键就相当于一个变量,我们使用一个变量存储一个10g的电影显然是不可能的。在上传请求中,将请求数据以二进制流的方式发送给服务器。
在ajax中如何发送二进制流数据给服务器- 创建
FormData的对象,将请求数据存储到该对象中发送 - 将
processData属性的值设置为false,告诉浏览器发送请求数据是对象 - 将
contentType属性的值设置为false,设置请求数据的类型为二进制类型。 - 正常发送ajax即可
- 创建
上传成功后后台服务器应该响应什么结果给浏览器- 在浏览器如何处理后台服务器处理完成后,响应一个json对象给浏览器,示例格式如下:
{ state:true,msg:“服务器繁忙”,url:”上传成功的资源的请求地址”}
- 在浏览器如何处理后台服务器处理完成后,响应一个json对象给浏览器,示例格式如下:
导入文件上传依赖的jar
<!--文件上传依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId>
<version>1.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.8.0</version>
</dependency>配置文件上传组件
<!--文件上传解析组件
id必须为multipartResolver
springmvc默认使用该id找该组件
-->
<bean
id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver">
</bean>10.1 准备用户表
CREATE TABLE `player` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`password` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`nickname` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`photo` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
`filetype` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;10.2 前端代码
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="js/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function(){
$("#uploadFile").click(function(){
// 获取要上传的文件
var photoFile =$("#photo")[0].files[0]
if(photoFile==undefined){
alert("您还未选中文件")
return;
}
// 将文件装入FormData对象
var formData =new FormData();
formData.append("headPhoto",photoFile)
// ajax向后台发送文件
$.ajax({
type:"post",
data:formData,
url:"fileUpload.do",
processData:false,
contentType:false,
success:function(result){
// 接收后台响应的信息
console.log(result)
// 图片回显
}
})
})
})
</script>
</head>
<body>
<form action="addPlayer" method="get">
<p>账号<input type="text" name="name"></p>
<p>密码<input type="text" name="password"></p>
<p>昵称<input type="text" name="nickname"></p>
<p>头像:
<br/>
<input id="photo" type="file">
<a id="uploadFile" href="javascript:void(0)">立即上传</a>
</p>
<p><input type="submit" value="注册"></p>
</form>
</body>
</html>10.3 controller
@Controller
public class FileUploadController {
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("fileUpload.do")
public String fileUpload(MultipartFile headPhoto) throws IOException {
// 指定文件存储目录
File dir = new File("d:/imgs");
// 获取文件名
String originalFilename = headPhoto.getOriginalFilename();
// 文件存储位置
File file =new File(dir,originalFilename);
// 文件保存
headPhoto.transferTo(file);
return "OK";
}
}10.4 文件上传的问题
中文文件名编码问题- 通过过滤器解决
文件位置存储问题- 放在当前项目下,作为静态资源,这样可以通过URL访问
- 在SpringMVC中配置静态资源放行
// 指定文件存储目录为我们项目部署环境下的upload目录
String realPath = req.getServletContext().getRealPath("/upload");
File dir = new File(realPath);
// 如果不存在则创建目录
if(!dir.exists()){
dir.mkdirs();
}文件名冲突问题(使用UUID)
// 获取文件名
String originalFilename = headPhoto.getOriginalFilename();
// 避免文件名冲突,使用UUID
String uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
// 获取文件后缀名
String extendsName = originalFilename.substring(originalFilename.lastIndexOf('.'));
// 拼接新的文件名
String newFileName = uuid.concat(extendsName);
// 文件存储位置
File file =new File(dir,newFileName);控制文件类型与大小
- 修改返回类型为
Map类型 - 添加前端对接收到的
message处理 headPhoto类型为MultipartFile,并且名称与前端传入FormData的key相同
// 控制文件大小
if(headPhoto.getSize() > 1024*1024){
map.put("message","上传的文件不能大于1m");
return map;
}
// 获取文件后缀名
String extendsName = originalFilename.substring(originalFilename.lastIndexOf('.'));
// 控制文件类型
if(!extendsName.equals(".jpg")){
map.put("message","文件类型只能为jpg");
return map;
}上传图片回显问题
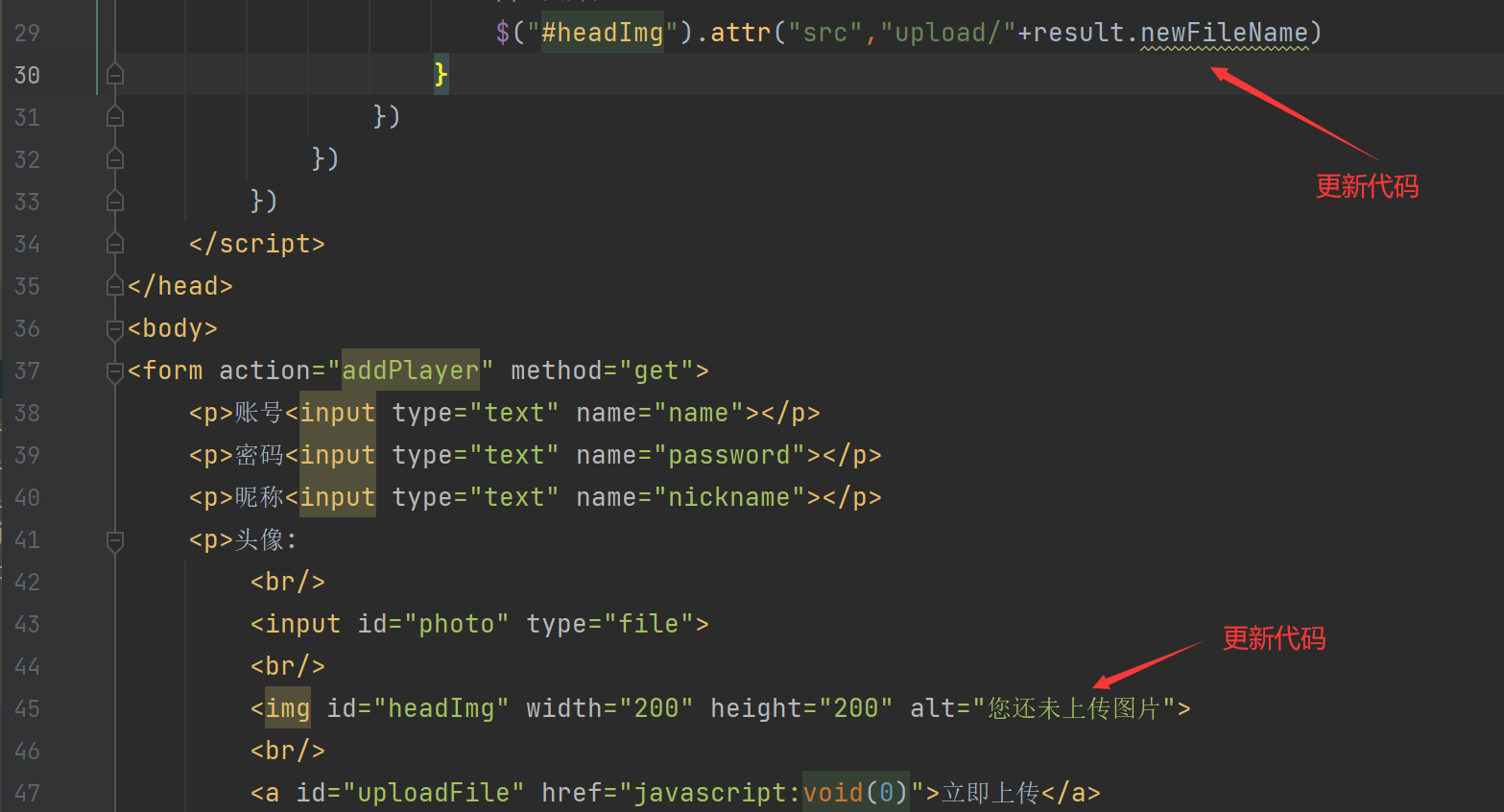
添加进度条- 见文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/wuyu1787/p/8919588.html ,这里不过多阐述
单独准备文件存储服务器